Benjamin Bloom revolutionised education when he helped develop the Taxonomy of Educational Objectives. At the time, Bloom was working with Edward Furst, Walter Hill, Max Englehart, and David Krathwohl to create a framework for organising educational objectives. Today it is often called Bloom’s Taxonomy. The framework is primarily used by teachers and professors to aid their students.
More about Bloom’s Taxonomy and its fundamentals can be found below.
What Is It?
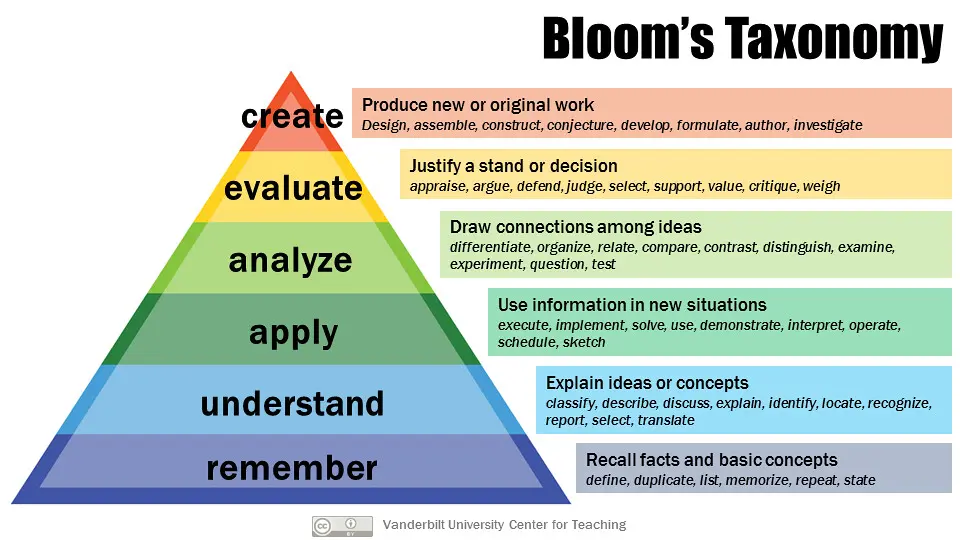
Although it can provide countless perks, Bloom’s Taxonomy is simple. It is a framework used to organise a person’s education goals. Generations of teachers and professors have used the framework to create better teaching plans for their students. The original framework created by Bloom and his team consisted of six categories, including Comprehension, Analysis, Evaluation, Knowledge, Application, and Synthesis.
As for the knowledge category, it can be broken down into specific abilities and skills. Nevertheless, knowledge was considered a requirement for using the skills in a practical sense. In 2001, the taxonomy was revised to help with more than educational objectives.
Taxonomy Was Revised In 2001
Bloom’s Taxonomy was revised in 2001 by a group of curriculum theorists, psychologists, instructional researchers, and testing specialists. It makes the taxonomy more general instead of focusing so much on education. Nevertheless, it still includes six categories, create, evaluate, analyse, apply, understand, and remember.
Regardless, the original goal was to help professors select more effective classroom activities. It can also achieve better metacognition. Using the taxonomy can be effective for teachers and students. More about the ways it can help will be provided below.
How Educators Use Bloom’s Taxonomy
Educators can use Bloom’s Taxonomy for numerous purposes. Typically, educators can create more effective study plans and pick better classroom activities by using this theory. For instance, they will be able to identify learning outcomes and assess the progress of their students.
Identifying Outcomes
Each teacher needs to develop a plan for each student. Otherwise, their universal plan may not work effectively for every student. Some will end up being left behind. Bloom’s taxonomy is helpful because it can be used to find out what the student should learn in class. It will also identify the order in which the student will learn the topic. The professor should make these objectives clear from the beginning.
Then, the student will know where they’re going and how they’re going to get there. Although this seems like a small change, it can make add weight to each assignment. In some cases, it is best to use Bloom’s taxonomy to create weekly objectives for the students.
Defining Effective Activities
Professors can use Bloom’s taxonomy to define effective classroom activities. Once the end objectives have been identified, it is essential to find out how to achieve these goals. Bloom’s framework can be helpful for planning coursework and homework to help the student reach these goals. Educators will find that it is very successful to use a combination of assignment types, including team-based studies, problem-solving lessons, and curation.
They can even create videos and podcasts to help their students. Regardless, Bloom’s Taxonomy makes it easier for teachers to choose classroom activities that will be effective for pushing their students closer to their goals.
Studying Progress
To achieve the desired goals, the professor needs to make sure that the student is progressing nicely. If this isn’t happening, they’re likely going to fall behind. It is essential to find ways to measure the student’s progress to ensure they’re moving forward. The framework allows the teacher to create weekly objectives and ensure that those weekly objectives are achieved. They can use this to make sure that the student is getting closer to achieving the curriculum’s bigger goals.
Challenges Students
Bloom’s Taxonomy is not suitable for all grade levels. However, educators have discovered that the framework can urge young students to challenge even the most basic skill. In other words, taxonomy encourages students to push past basic skills to learn on a more complex level. The end result is a higher order of thinking.
Teachers are all about their students challenging themselves academically. Bloom’s Taxonomy may push the next generation of students to become more creative and critical thinkers. If this is the case, impacted students are almost guaranteed to excel in college and beyond.
Young students may not initially appreciate Bloom’s Taxonomy but over time, they will begin to realise its value.
Should Bloom’s Taxonomy Be Used?
While there are limits to Bloom’s Taxonomy, it is still helpful in many situations. Ultimately, the goal is to help professors identify, diversify, and specify their learning objectives. Once this happens, the teacher can begin developing a plan to guarantee that these objectives are accomplished. Although it might not be perfect, the framework will still prove to be valuable to many people in the educational sector.
Utilising The Different Levels Of Bloom’s Taxonomy
It is no big secret that Bloom’s Taxonomy has been edited and updated over the years. While that was mentioned earlier, the most important thing is the way in which the theory is utilised for learning. It doesn’t matter as long as students start at the bottom and build their way toward the peak.
Tackling the theory, like building a home, will prove extremely useful in your student’s future endeavors. The framework is always designed in a way where the previous material will only contribute to the next material.
Therefore, approaching this task like building a home will only help your students develop a strong foundation to fall back on. While students learn at different rates and some adapt better in different areas, spending a little extra time near the bottom will only prove useful for future learning endeavors.
Summary
Bloom’s Taxonomy has become a staple of the education system because it helps professors develop more effective study plans. It makes designing courses easier while ensuring that the student learns, remembers, and understands the subject. Ultimately, the goal is to identify and specify the educational goals for the student. It also makes it possible to assemble classroom activities to ensure that these objectives are achieved.
Author Profile
-
My first experience of teaching was in 2016, when I was asked to
deliver a talk to a group of 16-year-olds on what it was like to start
your own business. I immediately knew I wanted to become more
involved in teaching but I didn’t know where to start as I had not
previously considered a career in education. A few weeks later I
agreed to teach a class of Chinese students from the Shanghai
Technical Institute of Electronics and Information, who had travelled
to the UK to learn English and Software Engineering, after that I was
hooked. Within the next few years, I taught hundreds of students of
many different nationalities, aged from 16 to 60, and from
levels 2 to 6. I focused my time teaching with Bath University and
Bath College for several more years until I felt a change was in order.
For the last few years, I have taught remotely with several private
training organisations, provided dedicated one to one coaching
sessions, provided consultancy on teaching and assessment practices
and written about my experiences as a teacher. I plan to continue
with my current activities for the foreseeable future but I’m always
open to new teaching experiences.

It was nice reading about you and how you started teaching… I was looking for theories and principles of assessment but didn’t’ chance to find them in the content below the heading… Was it lack of surfing skill or the content is not uploaded?
All the same I found paragraphs n how to use Blooms Taxonomy value adding.
Carole
Hi Carole, thank you for your message, I have an article on theories principles and models of assessment available at https://start-teaching.com/theories-principles-and-models-of-assessment/ if you’re having any difficulties accessing the content please get in touch [email protected] Thanks James